Develop a simple OPAC system for library using even-driven and concurrent programming paradigms of Java. Use JDBC to connect to a back-end database.
Procedure :
- Create a new Database file in MS ACCESS (our backend) named “books.mdb”.
- Then create a table named “Library” in it.
- The table Library contains the following fields and data types,
- AuthorName – Text
- ISBN – Text
- BookName - Text
- Price - Number
- Publisher – Text
- Enter various records as you wish.
- Save the database file.
- Next step is to add our “books.mdb” to the System DSN. To do that follow the procedure given below,
- Go to Start-> Control Panel -> Administrative tools.
- In that double click “Data Sources (ODBC)”.
- ODBC Data Source Administrator dialog appears.
- In that select “System DSN” tab and click the Add Button.
- Select “Microsoft Access Driver(*.mdb)” and click Finish.
- ODBC Microsoft Access Setup appears. In the “Data Source name” type “Library”.
- Click on the “Select” button and choose your database file. Then click ok.
Now your database file gets added to the System DSN. It should look like below,
Now execute the following code “Library.java”.
import java.sql.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.table.*;
public class Library implements ActionListener
{
JRadioButton rbauthor = new JRadioButton("Search by Author name");
JRadioButton rbbook = new JRadioButton("Search by Book name");
JTextField textfld = new JTextField(30);
JLabel label = new JLabel("Enter Search Key");
JButton searchbutton = new JButton("Search");
JFrame frame = new JFrame();
JTable table;
DefaultTableModel model;
String query = "select * from Library";
public Library()
{
frame.setTitle("Online Public Access Catalog");
frame.setSize(500,600);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
JPanel p1 = new JPanel();
JPanel p2 = new JPanel();
JPanel p3 = new JPanel();
p1.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
p1.add(label);
p1.add(textfld);
ButtonGroup bg = new ButtonGroup();
bg.add(rbauthor);
bg.add(rbbook);
p2.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
p2.add(rbauthor);
p2.add(rbbook);
p2.add(searchbutton);
searchbutton.addActionListener(this);
p3.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
p3.add(p1,BorderLayout.NORTH);
p3.add(p2,BorderLayout.CENTER);
frame.add(p3,BorderLayout.NORTH);
addTable(query);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
public void addTable(String s)
{
try
{
Class.forName("sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver");
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:odbc:Library","","");
Statement st = conn.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery(s);
ResultSetMetaData md = rs.getMetaData();
int cols = md.getColumnCount();
model = new DefaultTableModel(1,cols);
table = new JTable(model);
String[] tabledata = new String[cols];
int i=0;
while(i<cols)
{
tabledata[i] = md.getColumnName(i+1);
i++;
}
model.addRow(tabledata);
while(rs.next())
{
for(i=0;i<cols;i++)
tabledata[i] = rs.getObject(i+1).toString();
model.addRow(tabledata);
}
frame.add(table,BorderLayout.CENTER);
conn.close();
}catch(Exception e){}
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent evt)
{
if(rbauthor.isSelected())
query = "select * from Library where AuthorName like '"+textfld.getText()+"%'";
if(rbbook.isSelected())
query = "select * from Library where BookName like '"+textfld.getText()+"%'";
while(model.getRowCount()>0)
model.removeRow(0);
frame.remove(table);
addTable(query);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
new Library();
}
}
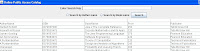
Screenshots of Output :
(Opening Screen)
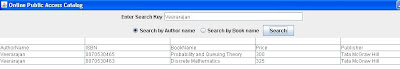
(author Search)
 (Book Search)
(Book Search) 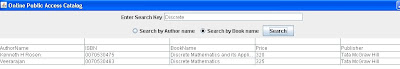
Download the Source Code
Library.java
books.mdb

